Shimizu Corporation was founded in 1804. The company began when Kisuke Shimizu I, who was a carpenter in Etchu or what is now Toyama Prefecture, launched the business in the Kanda Kajicho district of Edo (now Tokyo). From the moment the company was founded, Kisuke Shimizu I aspired to wholeheartedly devote himself to the company’s work and create quality reliable structures. Today, Shimizu continually delves deeply into knowledge and technology to meet the needs of its clients and, by extension, society.

- Corporate Name:
- SHIMIZU CORPORATION
- Head Office:
- 2-16-1 Kyobashi, Chuo-ku, Tokyo 104-8370
- Tel.:
- +81-3-3561-1111 (Main line)
- President and Representative Director:
- Kazuyuki Inoue
- Capital:
- JPY 74,365 million

Founding
In1804 by Kisuke Shimizu
Number of employees
10,845
as of March 31, 2023
The number of consolidated employees is 19,869.
Lines of Business
Construction, Architecture, Civil Engineering and Property Services
(General Construction Business)
Construction Business Licenses:Issued by the Minister of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism
(Special-1) No. 3200
(General-1) No. 3200
Construction Business
Real Estate Development and Other Businesses
as of September 1, 2023
Introductory Video

Shimizu Now
- View Video
- 9:29
Access
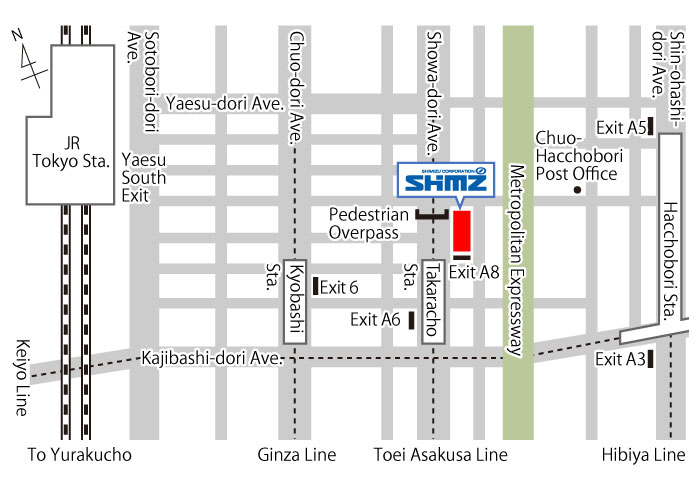
- Address:
- 2-16-1 Kyobashi, Chuo-ku, Tokyo 104-8370
- Tel.:
- +81-3-3561-1111 (Main line)
- Closest Stations:
-
- Toei Asakusa Line, Takaracho Station (Exit A8): Nearby
- Tokyo Metro Ginza Line, Kyobashi Station (Exit 6): 5 minute walk
- JR Line, Tokyo Station (Yaesu South Exit): 10 minute walk
- JR Line/Tokyo Metro Hibiya Line, Hatchobori Station (Exits A3 and A5): 10 minute walk
History
- 1804:
- Founder Kisuke Shimizu I establishes the company in Kanda Kajicho, Edo (present-day Tokyo).
- 1937:
- Reorganized as Shimizu Gumi, Ltd.
- 1948:
- Renamed Shimizu Construction Co., Ltd.
- 1962:
- Shares listed on First Section of the Tokyo Stock Exchange.
- 1991:
- Seavans is completed in Minato-ku, Tokyo and the head office is moved there from Kyobashi.
- 2003:
- 200 years since Shimizu was established.
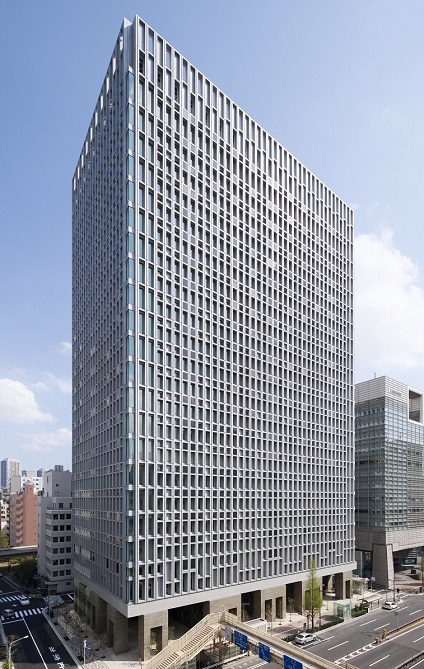
- 2012:
- Completed new head office in Kyobashi, Tokyo.
Past, Present, and Future of Shimizu Corporation
1804-1945: From the founding until after World War II ended, when the foundation of the company was built
Kisuke Shimizu I and Kisuke Shimizu II, who built the foundation of Shimizu
In 1804, Kisuke I, who launched the business in Edo, was recognized for his superior skills and selected to help build the West Wing of Edo Castle. Kisuke II designed and built the Tsukiji Hotel, Japan’s first western-style hotel, in 1868. They built the foundation of the company through their spirit of innovation and superb technical skills.
Tokyo Mokkoujou Arts & Crafts Furnishings opened with the technical craftsmanship passed down from ancient times
In 1884, a lumber cutting and assembly facility (now Tokyo Mokkoujou Arts & Crafts Furnishings) was opened in what is now Kiba, Koto-ku, Tokyo. Shimizu is the only major construction company to have its own wood-processing facility.


The first drafting office in Japan's construction industry
Around 1887, a drafting room was established to develop personnel capable of drafting Western architectural designs. This was the precursor of today’s Design Division.
The first R&D facility in Japan's construction industry
Shimizu Corporation had been putting efforts into research and development since before World War II. In 1944, in the middle of the war, a research center was established within the Design Division. This was the first R&D center in the industry.

1946-2000: Technological innovation and taking on the challenge of leading edge technology
Taking on the challenge of the unprecedented suspension roof ? Yoyogi National Stadium
Yoyogi National Stadium was built in 1964 for the 18th Olympics in Tokyo. The suspension roof structure used for the external complex curved surface was something rarely seen in the world at that time.

Japan’s first underground LNG storage tank built, heralding a new era in energy
In 1970, Japan’s first underground LNG storage tank (capacity, 10,000 kl) was built on the premises of the Tokyo Gas Negishi Terminal. The propelling force behind this was the transition to clean energy.
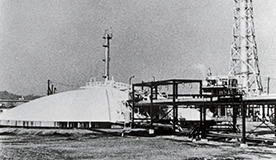
Tokyo Gas Negishi Terminal
Japan’s first seismic isolation retrofit in renovation of the National Museum of Western Art
This art museum was designed by Le Corbusier and build by Shimizu Corporation in 1959. In 1998, the museum was renovated with Japan’s first seismic isolation retrofit. Shimizu succeeded in securing anti-seismic performance while preserving Le Corbusier’s original design.

2001 onward: Looking toward the future of the construction industry
Success in building Japan’s first zero energy building (ZEB) ? Seicho-no-Ie’s Office in the Forest
In 2013, Shimizu succeeded in building a zero energy building in Hokuto-shi, Yamanashi Prefecture that made maximum use of natural energy adapted to the specific characteristics of the region. We are aiming to achieve ZEB in a mid-rise building in 2018.
Taking on the challenge of ZEB
Strong and flexible, facilities and community planning that are people-friendly and easy on the environment
In 2012, a smart community was created in the Kyobashi area, with the newly opened Kyobashi head office as its nucleus. The Kyobashi Smart Community Council was established, and ISO 22301 (Business Continuity Management Systems) and ISO 50001 (Energy Management Systems) certifications were acquired for an entire community block, for the first time in Japan.

Shimizu Smart Site, a Next-generation Production System for Building Construction was Developed
Shimizu began full introduction of the Shimizu Smart Site in 2018. This system uses autonomous robots equipped with the latest technology to work alongside humans in performing construction. We are aiming to improve the working environment, increase productivity, and create job sites that attract young people and make them want to work at them.