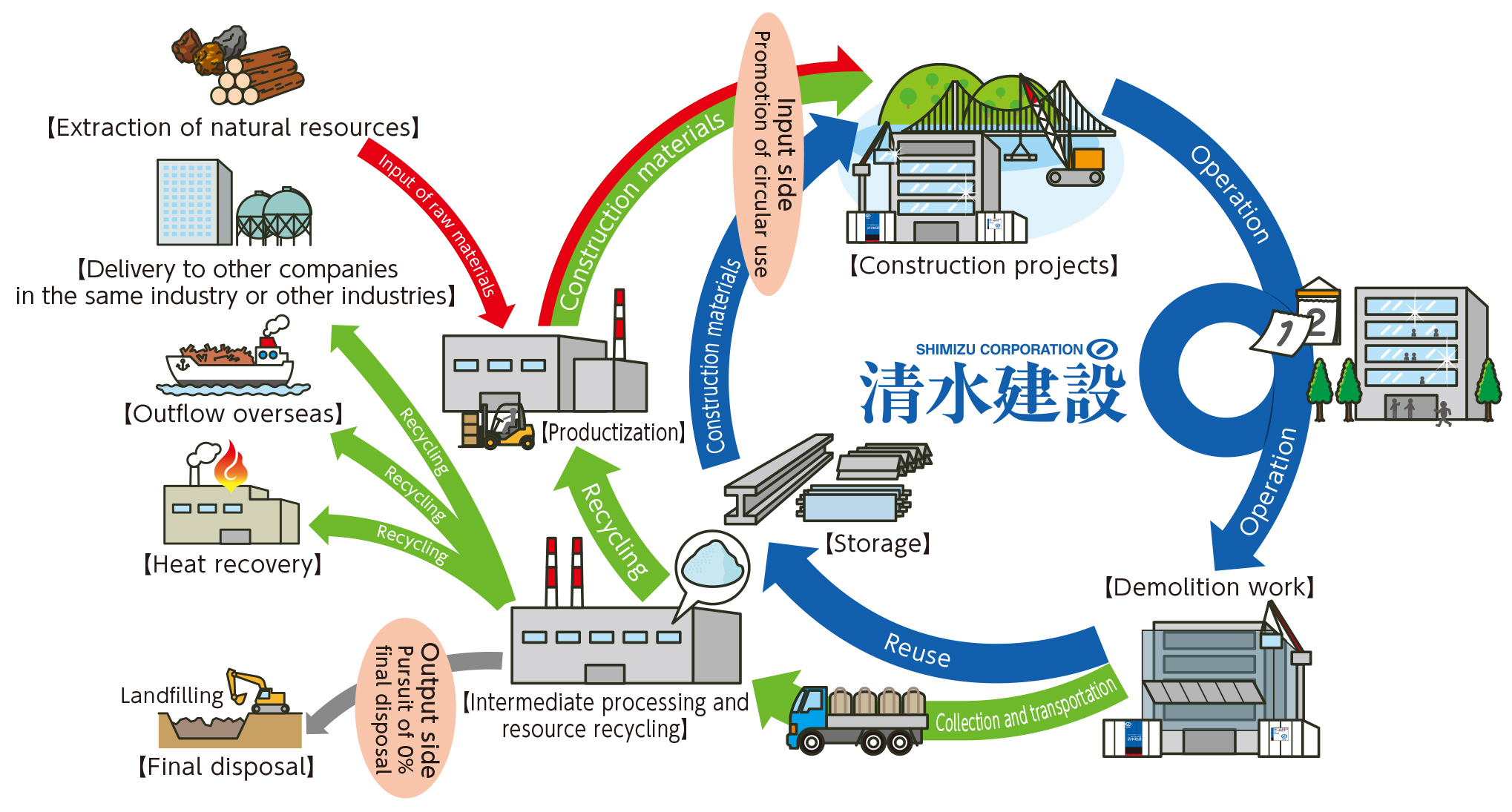
We have adopted business activities with low environmental impact as our Environmental Basic Policy. In our construction projects, we have positioned the prevention of environmental pollution as a key management priority and have promoted the 4R activities (refuse, reduce, reuse, and recycle) to conserve resources and reduce and recycle by-products.
In the resource recycling roadmap published in FY2025, we set, in addition to the output-side target of achieving a final disposal rate of 0% for construction by-products by 2050, a new management target: the input-side recycling utilization rate. We established goals of 25% or higher by 2030 and 50% or higher by 2050.
To achieve these targets, we will promote the procurement of construction materials that take recycled content into account, along with design and construction practices that anticipate future reuse and recycling.
Over the longer term, through business development focused on resource productivity, including creating greater value with fewer resources, including construction practices that minimize the use of natural resources, we aim to help realize a sustainable society while generating new business value.
Resource Recycling and Waste Reduction
Quantifying the Input-side Recycling Utilization Rate
Promoting resource recycling (the circular economy) is a key responsibility for construction companies. We calculate the input-side recycling utilization rate (the proportion of circulated materials within the materials brought into our construction projects) based on the government’s Fundamental Plan for Establishing a Sound Material-Cycle Society. We have set medium- to long-term targets of at least 25% by 2030 and at least 50% by 2050.
We will continue to measure this rate regularly in our construction projects and work to improve it across all processes, including design, procurement, and construction, thereby actively contributing to the promotion of resource recycling.
Fundamental Plan for Establishing a Sound Material-Cycle Society
Target Values for the Input-side Recycling Utilization Rate
| 2030 | 2050 | |
|---|---|---|
| Construction Work (Building and Civil Engineering) | 25% or more | 50% or more |
Definition of the Input-side Recycling Utilization Rate
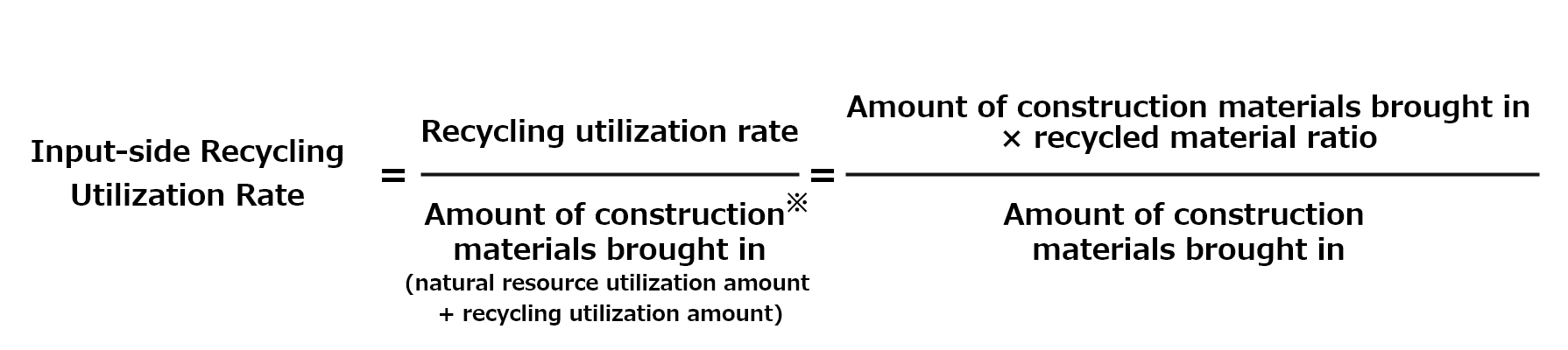
Calculation of the Input-side Recycling Utilization Rate
- FY2024 Input-side Recycling Utilization Rate
21%
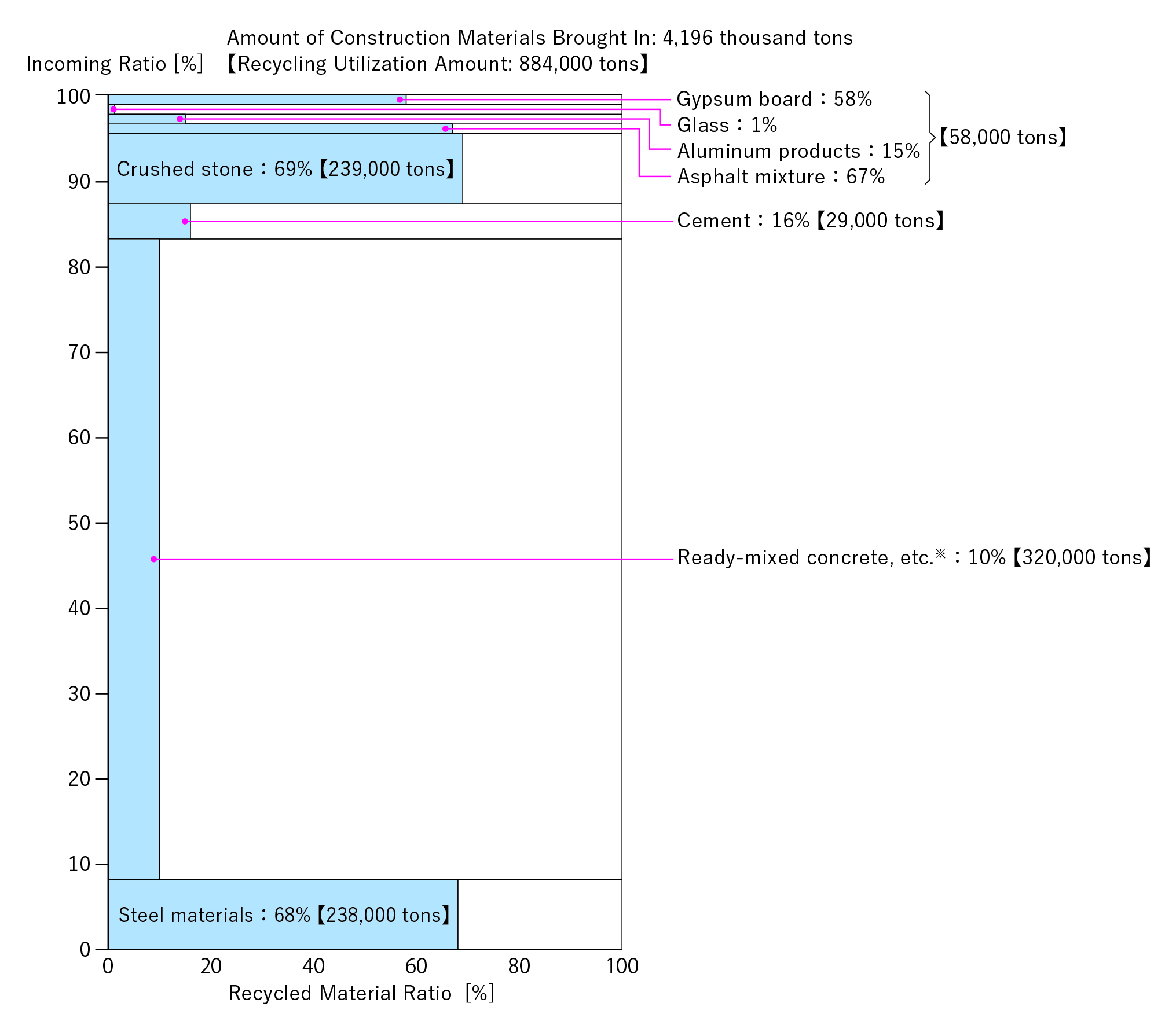
Cement used for ready-mixed concrete is recorded under “ready-mixed concrete, etc.”
Cement used for ground improvement materials and on-site mixed concrete is recorded under “cement."
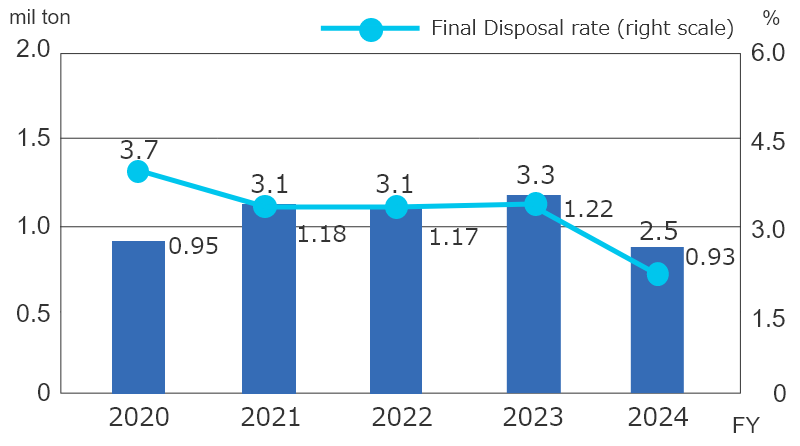
Total Emissions and Final Disposal Rate
We aggregate annual construction waste data from our worksites using Shin-Kan-Tasu, our construction by-products data management system. We manage performance against our KPI of reducing the final disposal rate.
To ensure proper waste disposal and to align with the government’s digitization policy, we are promoting the use of electronic manifests. The adoption rate reached 97% in FY2024.
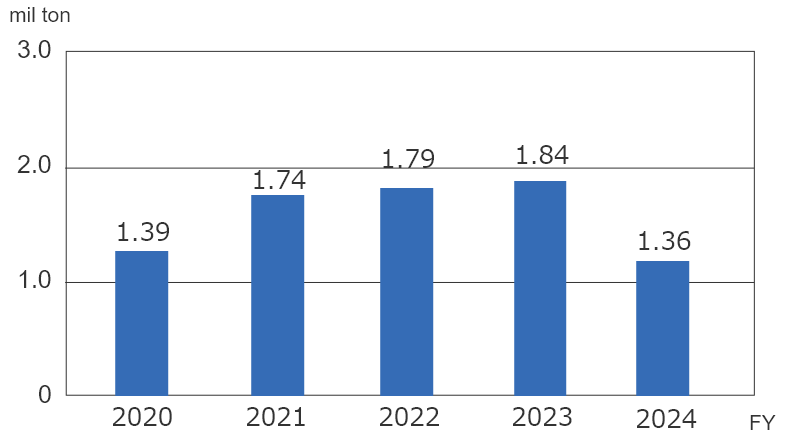
The FY2024 results are as follows.
- Total volume generated:
1.36million tons (26% YoY)
- Volume generated (excluding sludge):
0.93million tons (-24% YoY) - Final disposal rate:
2.5% [Target: 3.5% or less]
Specific initiatives and measures
4R Activities at Worksites
We plan and pursue 4R activities and are working to use fewer resources, reduce the volume of by-products, and recycle resources. We also employ a system for predicting the volume of construction by-products that will be generated, and formulating and implementing a plan for effective reduction.
Shimizu also provides e-learning on proper processing of construction by-products, education in environmental risk management for the general managers and foremen of construction sites, and works to comply with laws and regulations at job sites, control the volume of by-products generated, and recycle resources.
- RefuseGoing package-less, precutting at the factory, and unitization
- ReduceUsing alternate formwork and industrialization at job sites to reduce use
- ReuseReusing repetitive formwork (eco formwork) and improved soil
- RecycleBringing materials to a recycling center so they can be reused, recycling by manufacturers (regional authorization, etc.)



Encouraging Manufacturer Recycling Using a Region-wide Certification System
We are promoting the use of the Wide-area Certification System (manufacturer recycling). We collect construction material waste generated at our worksites—such as gypsum board and urethane materials, including product offcuts—and ensure proper processing through recycling at manufacturers certified by the Minister of the Environment.
In addition to gypsum board, which had a high utilization rate under the system, beginning in FY2024, we also collect rock wool sound-absorbing panels, glass wool, and other materials at transfer points using NRBOX, a dedicated collection container provided by Nippon Express Co., Ltd., and ship them directly to manufacturers.
We will expand this initiative to additional worksites and collaborate with other companies to implement circular collection, thereby contributing to the promotion of resource recycling across the construction industry.



Material Recycling of Waste Plastics
We are promoting the material recycling of plastic waste generated at construction sites. At our sites, Green Masters (waste management specialists) use plastic sensors to conduct advanced sorting of many types of plastics and have established a scheme for selling the sorted materials as valuables. In the initial deployment, approximately 4,000 m³ of waste plastics have been designated for sale.
We have also launched “Site to Site” material recycling, in which waste plastics generated at a given site are reused at the same site as raw materials for new building materials. Going forward, we will expand our efforts to promote the material recycling of waste plastics not only in Tokyo but also in regional areas.



News Release
- Recycling diverse waste plastics generated at construction sites
- Reusing waste plastics generated at construction sites as new building materials
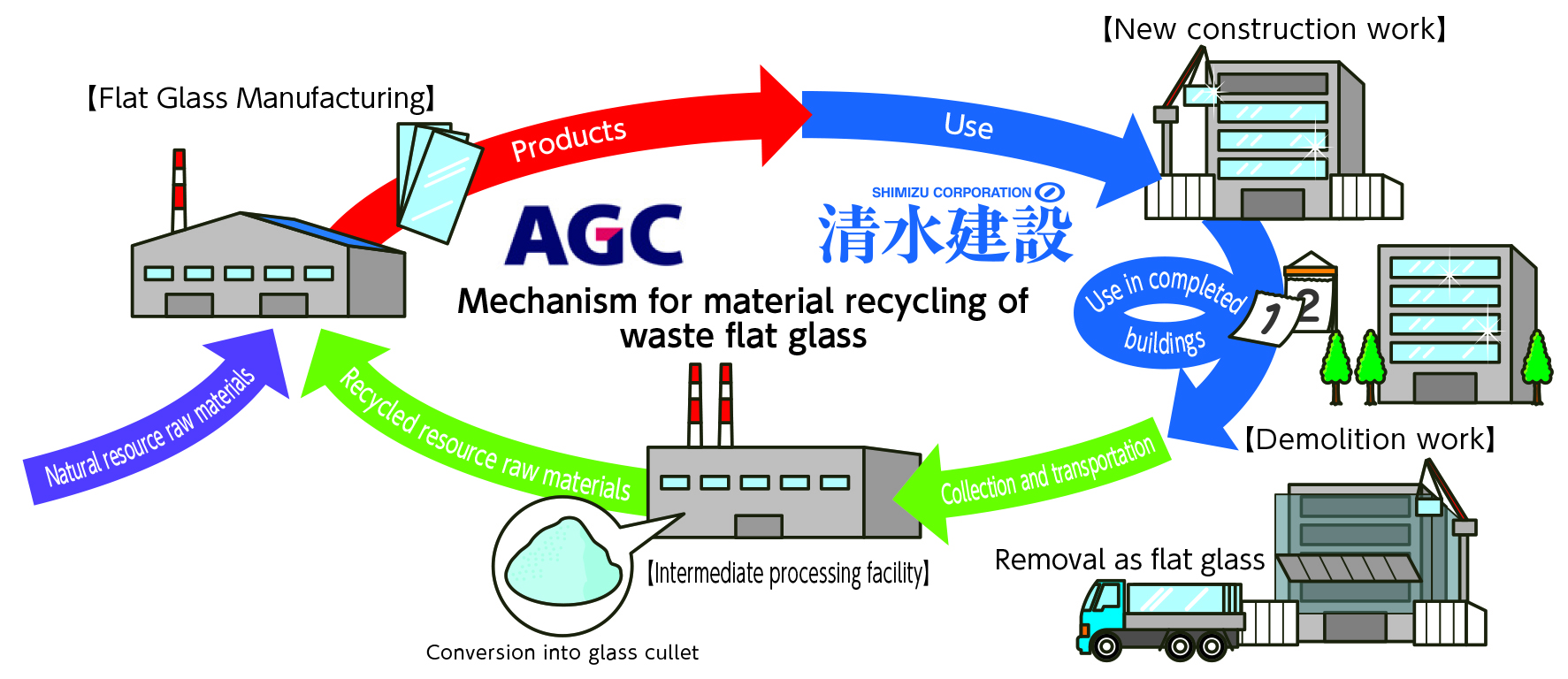
Recycling Flat Glass from High-Rise Buildings
Waste flat glass generated during the demolition of super high-rise buildings has historically been difficult to recycle, resulting in most of it being sent to landfill. At one of our construction sites, we recovered about 90% of the roughly 340 tons of exterior glass removed from a demolished building, keeping it in flat form and recycling it as material for new glass products.
The recovered glass is sorted and purified at a recycling plant to remove impurities and then processed into cullet. The cullet is supplied to the glass manufacturing plant of AGC Inc., where, after quality testing, it is used as raw material for new flat glass.
We will continue to promote the material recycling of waste flat glass, particularly in demolition projects for super high-rise buildings.
News Release
Examples of resource-saving initiatives
Easily Removable Exhibition Hall for 100% Recycling
Construction of a Temporary Exhibition Hall on the East Side of Tokyo Big Sight (Tokyo Branch)
Shimizu diligently implemented 4R activities from the design and construction stage by preemptively considering the dismantling and removing of the building. In the construction stage, we applied various methods such as the steel pipe pile rotation and press fit method or our patented pile head ring socket construction method. We used precast concrete for the framework and unitized equipment during the construction stage, simplified packaging, and sorted waste, thereby substantially reducing generation of by-products. We also used recyclable materials for the exterior components and materials. We planned and implemented a 4D process using BIM, and employed environmentally friendly methods in the dismantling stage as well. Shimizu received a contributor's award from the Prime Minister for practicing the 3Rs (reduce, reuse, and recycle) in fiscal 2017 in this project.


Pollution Prevention
Shimizu endeavors to properly manage and prevent environmental pollution as an important component of management.
Asbestos
We are responding reliably to prevent pollution in terms of the asbestos generated from our demolition and renovation work. In particular, we are the only major construction company to develop and deploy the certified ASP construction method for the removal of friable asbestos.
We generated 7.744 t of friable asbestos from our demolition and renovation work in FY2022.
We have developed various original technologies as individual technologies. These include a real-time measurement device (FS-1), a volume reduction device (Shico) and an anti-scattering agent (Astector). In addition, we are encouraging our employees to obtain various asbestos-related qualifications. The revised Ordinance on Prevention of Health Impairment due to Asbestos and Air Pollution Control Act to go into effect in October 2023 will make it obligatory for a qualified person to conduct an asbestos building material survey in demolition and renovation work. Accordingly, we are providing all-in-one and intensive in-house courses to obtain the qualifications to serve as investigators for buildings and asbestos. In conjunction with obtaining qualifications, we are enhancing our employees' knowledge of asbestos building materials and further improving management capabilites to prevent contamination and health damage.


Dioxins, PCBs, CFCs, Halons, Noise and Vibration
Shimizu developed and is deploying the S-DA processing method to remove contamination from dioxins. Of the
waste containing high concentrations of PCBs stored by Shimizu, we completed processing of PCB-contaminated
machinery to render it harmless in fiscal 2019.
We held meetings with disposal contractors for the PCB contaminants we possess. We completed the detoxification
process in FY2021.
We conducted inspections and surveys on the fluorocarbons of the equipment we manage in accordance with the revised fluorocarbon law, and confirmed proper management. Furthermore, through our internal environmental audits as constructors, we verify that our management of waste CFC emissions from special equipment used during building demolition is being managed properly.
Shimizu has also developed and uses the Cool Cut method to control the generation of noise, vibration, and dust during the demolition process.
We will continue to work on preventing contamination by utilizing these measures and technologies.
Solution: Shimz Coolcut (Low Noise and Low Vibration) (only in Japanese)

Soil Remediation
We work to prevent soil environment issues before they occur and to stop contamination by efficiently and effectively utilizing a variety of countermeasure technologies that are effective in purifying contaminated soil.



