December 26, 2025
Shimizu Corporation (President: Tatsuya Shimmura) has developed a Spray-based 3D concrete printing system designed for the construction of large, curved reinforced components. The system integrates a nine-degree-of-freedom gantry robot with a material spray simulator that enables verification of sprayed-material behavior in advance. This enables highly accurate, automated fabrication of reinforced structural components and large components with complex geometries, applications that were difficult to realize using conventional material extrusion printing. The material spray simulator incorporated into the system was jointly developed with the Computational Engineering and Robotics Lab (CERLAB), led by Professor Kenji Shimada of the Department of Mechanical Engineering at Carnegie Mellon University.
As the decline in the working-age population driven by Japan’s aging society and low birthrate emerges as a major social challenge, the construction industry faces an urgent need for automation and labor-saving construction methods. In concrete construction, 3D printing is expected to move into practical use, and field applications have progressed primarily through material extrusion printing, in which cementitious materials are deposited layer by layer as they are extruded downward. However, this method makes it difficult to integrate rebars into the printed layers, thereby limiting its applicability to reinforced structural components. Spray-based printing, which forms structures by spraying cementitious materials, is better suited to producing reinforced structural components. At the same time, the complexity of printer motion control has made it difficult to ensure sufficient fabrication accuracy, presenting a key technical challenge.
In the newly developed system, printing control parameters are determined by using a material spray simulator to derive optimal nozzle paths, spray distance, angle, speed, material discharge volume, and related conditions. This approach improves printing accuracy while minimizing defect rates. The gantry robot used for printing consists of a seven-degree-of-freedom arm suspended from a two-axis XY motion mechanism mounted atop a portal-type frame. The printable area spans 6 meters in depth, 4 meters in width, and 3 meters in height. From the nozzle at the arm tip, material can be sprayed in multiple directions across a wide range, allowing it to fill even the interior of reinforced assemblies. In demonstration tests, the system successfully fabricated a twisted curved wall, with both the lower and upper layers projecting outward from the center, measuring 2.5 meters in height, in just four hours.
Once 3D printing of structural components is implemented at construction sites, it is expected to advance labor saving and workforce reduction in construction production while also increasing design flexibility for structures. Looking ahead, Shimizu Corporation will continue developing technologies to further enhance 3D printing in construction and will pursue the goal of fully automating concrete construction.
≪For Reference≫
Spray-based 3D printing system (gantry robot)
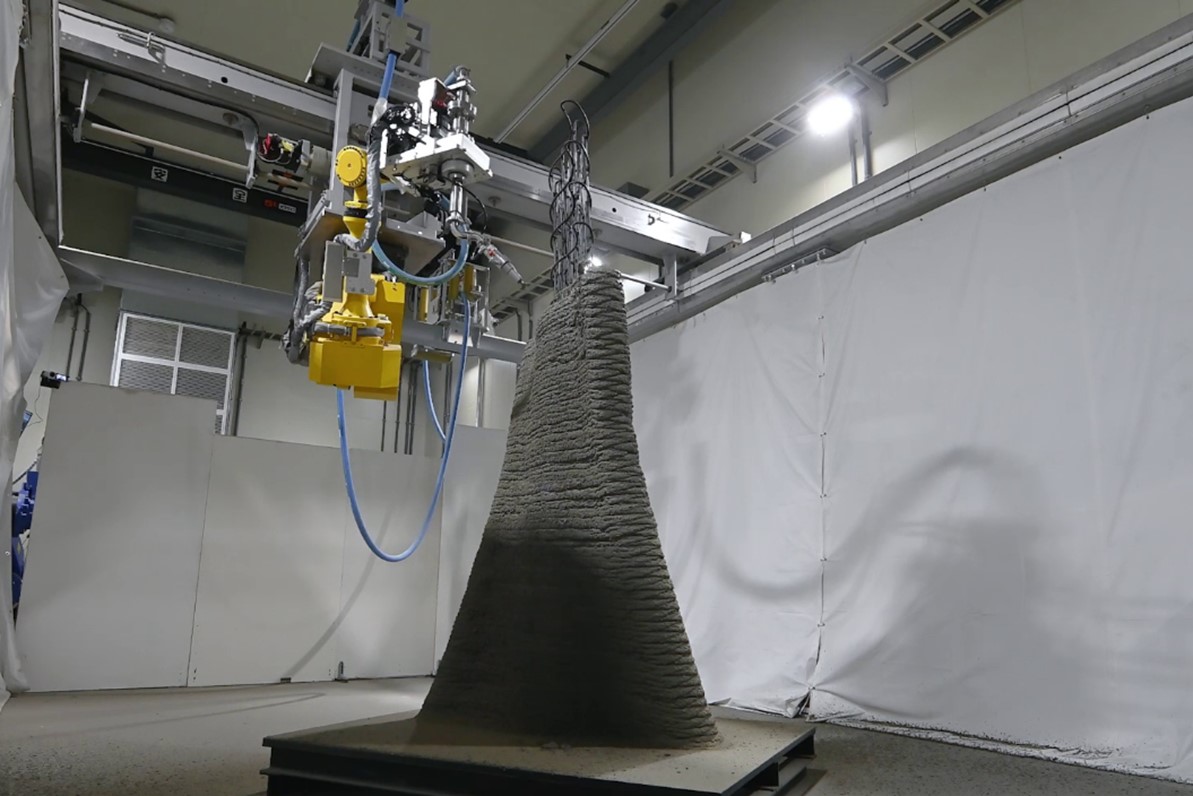

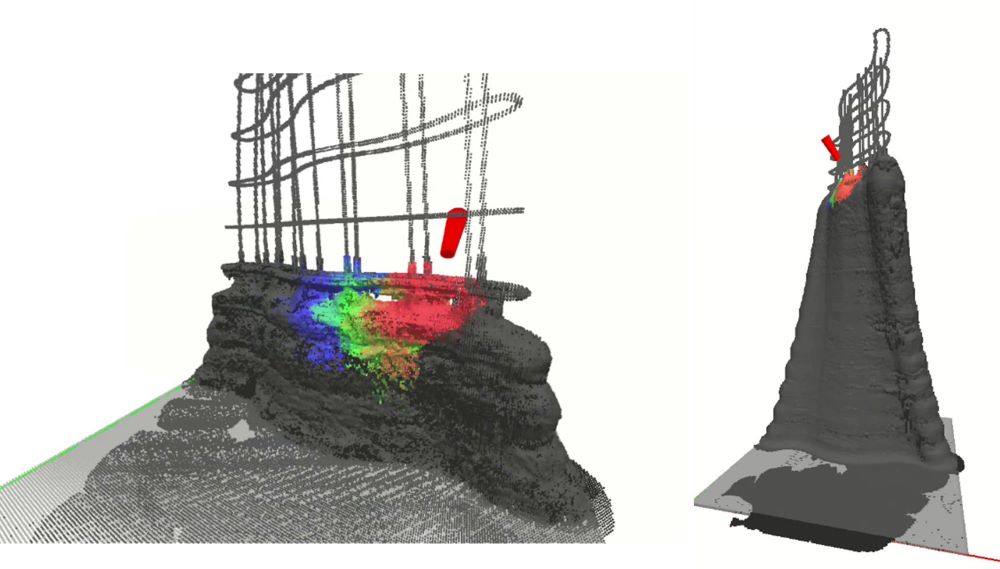
Demonstration test
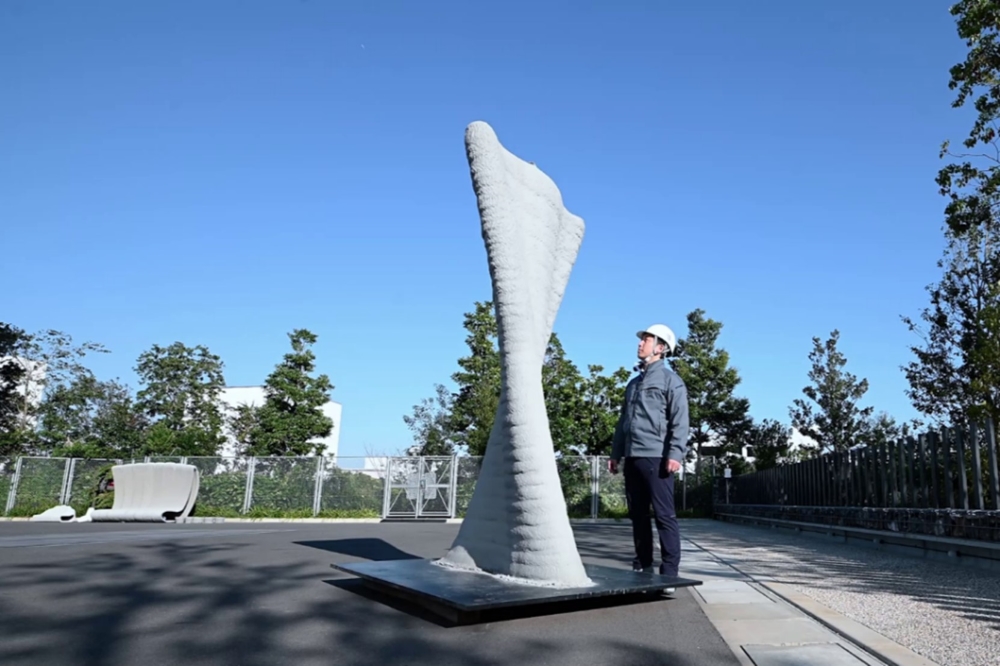


Technology introduction video
The information contained in this news release is the current information on the date of publication. Please be aware that this information may have changed by the time you view it. Please contact the company to inquire for further details.
