February 18, 2020
Shimizu Corporation (President: Kazuyuki Inoue, “Shimizu”) will complete demolition of the company’s old Hokuriku Branch office building currently underway in Kanazawa in March, and will begin construction of a new office building equipped with the highest energy- efficient performance in the Hokuriku region. The building will have one floor below ground, three floors above ground, and have a total floor space of approximately 4,100 m2. It is scheduled for completion in February 2021. Shimizu is aiming to make it the region’s first Zero Energy Building (ZEB) from the time the building is first used through the latest in energy-saving and power generation technology. This will enable a reduction in CO2 emissions of around 370 tons a year.
Shimizu employed the design concept of creating an office connected to the Hokuriku region and its future in planning the new office building, working to create an office building that utilizes new technologies. These technologies will connect to the future, achieve harmony with the history and traditions of Kanazawa, and contribute to workstyle reform and promotion of health.
The chief characteristic of the plan is the effort to utilize the latest energy-saving and power generation technology as new technology that will connect to the future and create a Zero Energy Building (ZEB). The new technologies that are core to the project encompass a wide variety of technologies, including equipment such as hydrogen utilization & storage equipment, solar power generation, radiant air conditioning, use of geothermal heat that utilizes a unique characteristic of the region, and natural airflow and lighting. These initiatives have been well-received, earning the rebuilding project recognition through selection by the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism (MLIT) as a leading project in CO2 reduction for sustainable buildings and selection by the Ministry of the Environment as a construction project using a self-sufficient, distributed energy system powered by hydrogen in fiscal 2019.
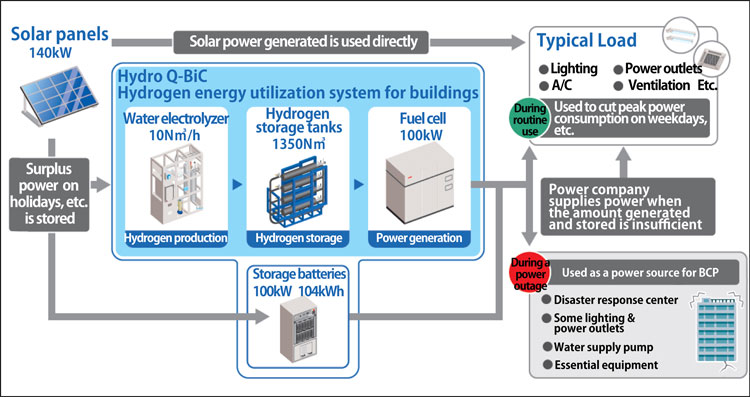
We used Hydro Q-BiC, a hydrogen energy utilization system for buildings, which Shimizu developed jointly with the National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST), for the hydrogen utilization & storage equipment. It is state-of-the-art technology that is essential for realizing the hydrogen-based society of the future. Its main characteristic is the use of surplus electricity generated from solar power to produce and store hydrogen, which is the ultimate form of clean energy, and then extract and convert it to electricity when needed to support business continuity planning (BCP) and when needed to generate power for other purposes. Many plans for buildings and communities that use hydrogen power generation are being launched in Japan, but the new office building for our Hokuriku Branch will be the first in the Hokuriku region to use hydrogen power generation and utilize hydrogen storage equipment having the largest storage capacity in Japan (2,000 kWh).
We also aim to achieve harmony with the history and traditions of Kanazawa and expressed this in an artistic finish suitable for a Machiya, traditional merchant’s house. We decided on a latticework finish for the exterior to achieve harmony with the remaining Machiya, traditional merchant’s houses in Kanazawa, and replicated the vertical wooden screens and coffered ceilings with modern technology. The characteristic latticework frames of the exterior serve the dual function of earthquake-resistant walls of the structure and will absorb 100% of the forces acting on the building during an earthquake. To create the coffered ceiling, we plan to use our newly developed fire-resistant wood and steel beams that use a combination of the Noto Japanese cypress produced in the prefecture and steel frame.
We are also working to create office space capable of accommodating the increasing need for diverse workstyles in the future by striving to create a share address workspace that enables users to work anywhere and by going paperless. Shimizu will continue to consider the adoption of new equipment to create office spaces that contribute to workstyle reform and promoting health in the future.
Shimizu will use the new office building for the Hokuriku Branch as a showroom during construction and thereafter to widely publicize the hydrogen utilization & storage equipment and other state-of-the-art technologies. We also intend to seek certification under the ZEB, WELL, and LEED certification systems after the building is in use to increase the value added by the building.
≪For Reference≫
Profile of the New Hokuriku Branch Office Building
| Location | 5-15 Tamagawa-cho, Kanazawa, Ishikawa Prefecture |
|---|---|
| Scale | One floor below ground, 3 floors above ground, 4,100 m2 in total floor space |
| Structure | Steel-reinforced concrete and partial steel frame |
| Construction period | April 2020 to February 2021 |
| Planning, design and build | Shimizu Corporation |

The exterior latticework framework around the building is modeled on the look of a Machiya, traditional merchant’s house and will also function as the earthquake-resistant walls of the structure.

Hydro Q-BiC Hydrogen Utilization and Storage System
The surplus electricity generated from solar panels (140 kW) during weekends and holidays when electricity demand is low is used to produce hydrogen. A metal hydride is then used to absorb the hydrogen and store it (2,000 kWh storage capacity). Hydrogen is extracted from the metal hydride and used to generate power on weekdays, when electricity consumption is high, or during an emergency. The reduction in CO2 emissions and maintenance and management expenses during routine operation are being measured and quantified for the administrative building in the Koriyama City, Fukushima Prefecture General Wholesale Market where the system is currently in use. The new Hokuriku Branch office building will be the first case of commercial use. (The numbers indicate the capacity of the equipment used in the new Hokuriku Branch office building.)
ZEB Certification
ZEB is the BELS (Building-Housing Energy-efficiency Labeling System) third-party certification label used in the system for indicating performance in terms of energy savings launched in April 2016, based on the Building Energy Conservation Act. The BELS system is operated by the Association for Housing Performance Evaluation and Indication. When a building achieves ZEB Ready status (energy savings of 50%), it is specifically labelled as such. Nearly ZEB is defined as energy savings of 75% or higher, and ZEB, as energy savings of 100%.
WELL Certification
WELL certification was established by the International WELL Building Institute (IWBI). It is an environmental certification system that focuses on health and well-being. Evaluation items are divided into 10 categories such as air and water, and buildings/spaces are rated according to three certification levels: Silver, Gold, and Platinum. More than 1,400 projects were registered worldwide as of February 2019. Fifteen projects were registered in Japan, and one has received certification.
LEED Certification
LEED certification is an environmental performance rating system developed and operated by the US Green Building Council (USGBC). It is used to rate the environmental performance of buildings and premises during operation. LEED is an acronym for Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design.
Vertical Wooden Screens (Kimusuko)
This description is used for the screens made of thin vertical wooden slats characteristic of Machiya, traditional merchant’s houses in Kanazawa. The Japanese word is pronounced as kimusuko or kimushiko.
Coffered Ceiling
A ceiling created by using lumber to create a square grid pattern and attaching boards to the back surface. It is an old architectural style used in Japanese architecture such as Buddhist temples and drawing rooms, and is used in formal rooms.
The information contained in this news release is the current information on the date of publication. Please be aware that this information may have changed by the time you view it. Please contact the company to inquire for further details.
