Building the Futuristic Hospital to Show the World
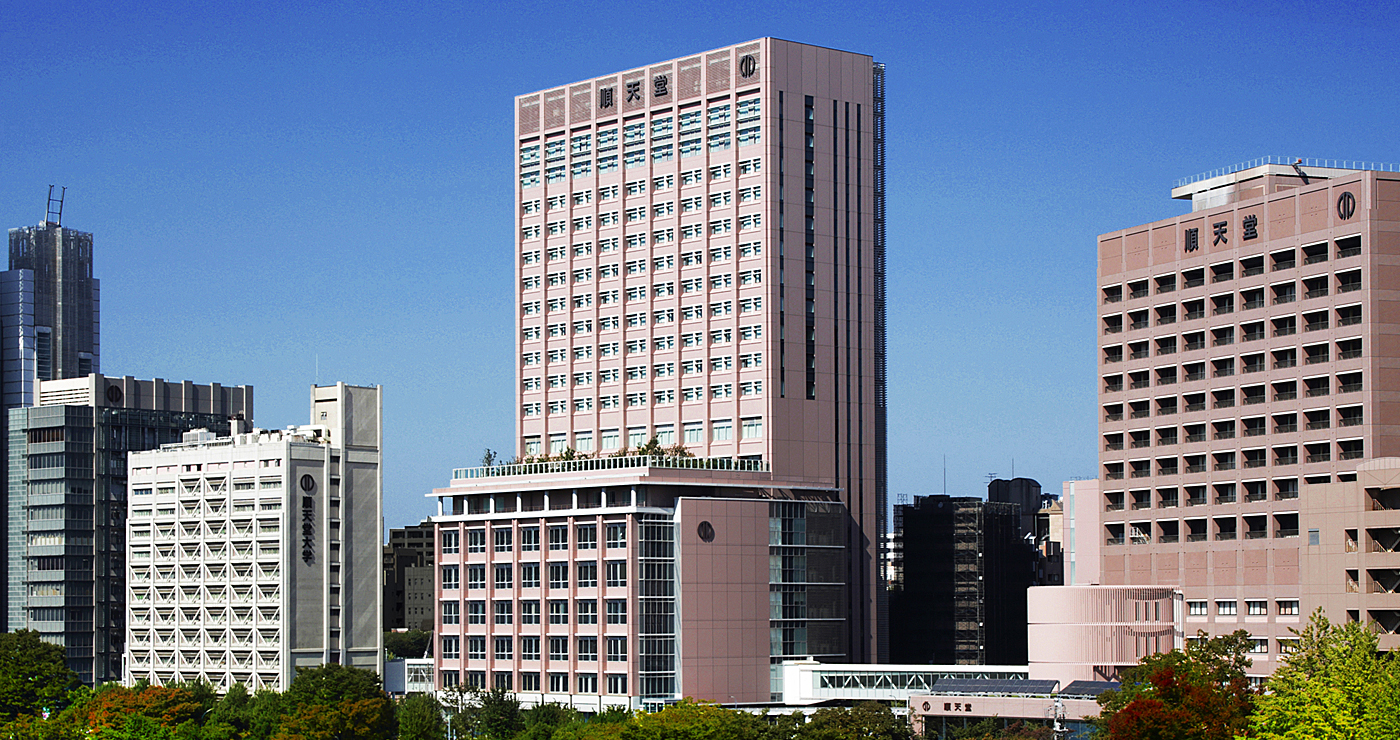
The group of buildings that make up Juntendo University Hospital stretch for several hundred meters along Sotobori-dori are a symbolic part of the Ochanomizu landscape in Tokyo. Although it is located in a city center, the nature along the bordering Kanda River bank and the greenery planted in the open spaces on campus have created a lush environment.
Building B, which is large and especially visible, was built in 2013 as part of the campus and hospital restructuring project to commemorate the 175th anniversary of the medical school’s founding. Juntendo and Shimizu assembled their knowledge and successfully built a futuristic hospital to show the world, based on the concepts of built to last 100 years, a hospital of the future that will be the model from this point forward, and an innovative initiative in ecological construction.
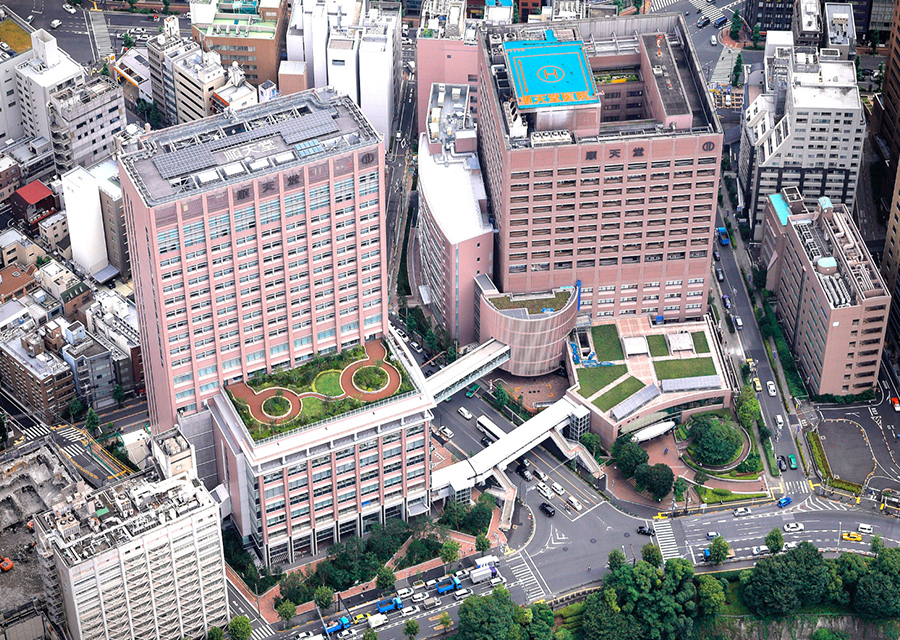

Using Advanced Structural Technology to Successfully Build a Safe Ultra-high-rise Hospital
The new building is an ultra-high-rise hospital that safely enables the continued functioning of the hospital even during an earthquake. This was achieved by combining a seismic isolation structure that minimizes the horizontal sway of the entire building with multiple technologies that minimize shaking on upper floors. The layout is functional with the examination area on the lower level where the structure has a large intercolumnar span. The wards were built on the higher levels, making it a hospital with magnificent views.
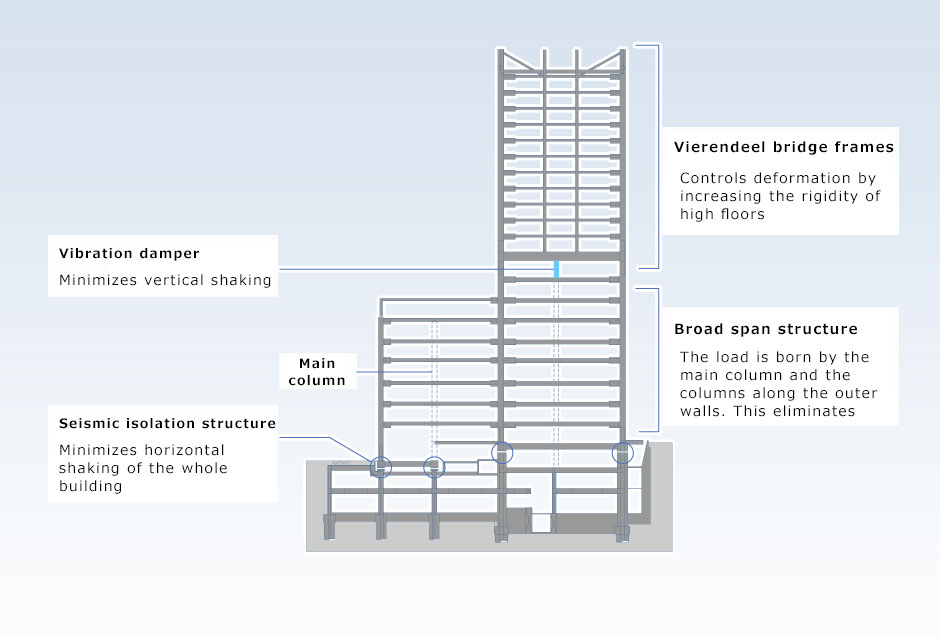
Optimal combination of structural technologies for an ultra-high-rise hospital
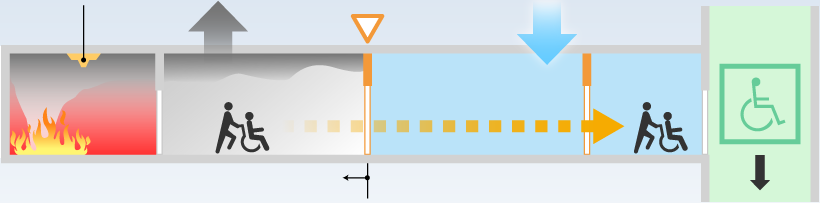
A fire evacuation system suitable for an ultra-high-rise hospital
We have also secured evacuation safety for an ultra-high-rise hospital to achieve higher level of safety. We developed and used a new technology, the SHIMIZU Hybrid Smoke Control System. It prevents patients from being harmed by smoke by controlling the air pressure in the corridors.
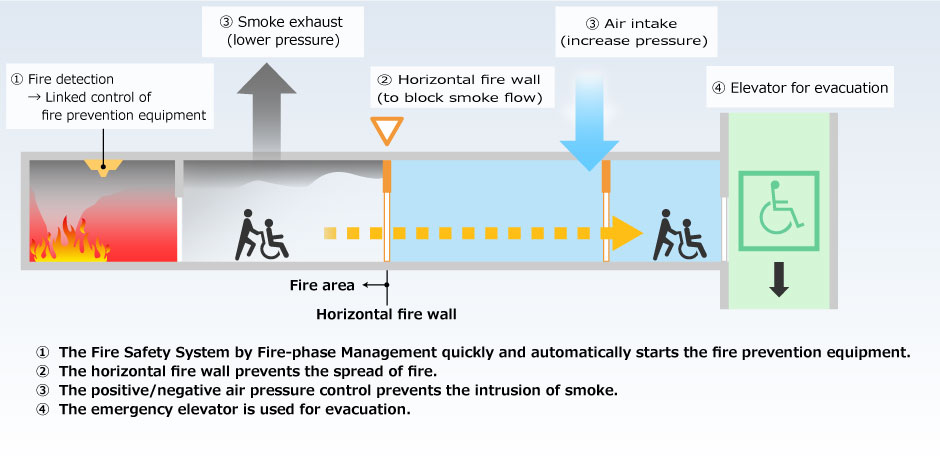
Diagram of the Fire Escape System
Advanced Infection Control Model
Infection control is an important issue for hospitals. We established advanced facility specifications for handling infectious diseases, based on the advice of the distinguished Professor Hori from the Juntendo University, who is an authority on infection control.
We created an environment that reduces the risk of airborne transmission with a combination of measures. Such measures include an air conditioning and ventilation system that minimizes the spread of airborne odors and contaminants and partitions between beds to prevention aerosolized transmission. Together, these cause the air to flow in one direction. We also developed a handwashing device that has little water spray to make it easy for the nurses to maintain hand and finger hygiene.
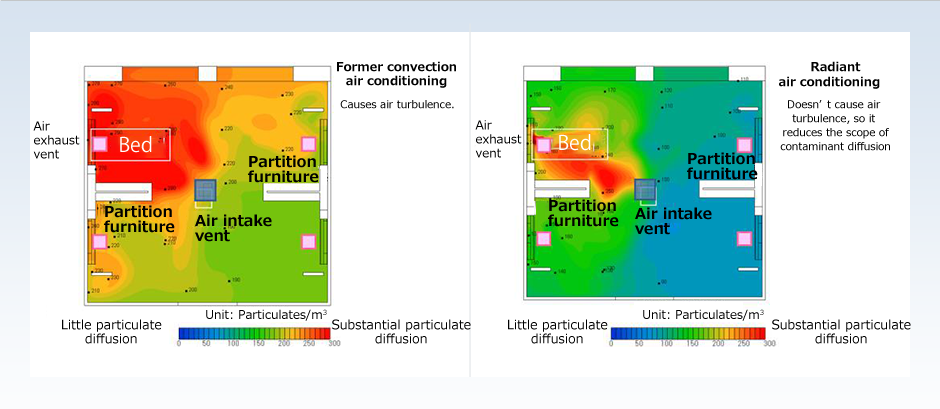
Devising ways to reduce the risk of airborne transmission

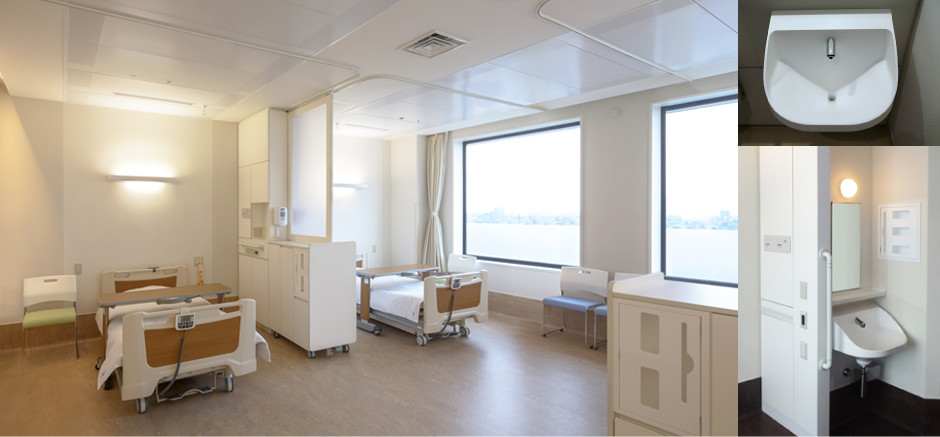
A 4-bed room with improved safety against infections
The furniture that serves as a partition between beds enables maintenance of patient privacy.
Handwashing device with little water spray
(Developed by Shimizu)
A patient-friendly hospital
All hospital rooms on the upper floors have magnificent views. The mid-level rooftop garden also provides a restful space for patients and family members within the hospital.
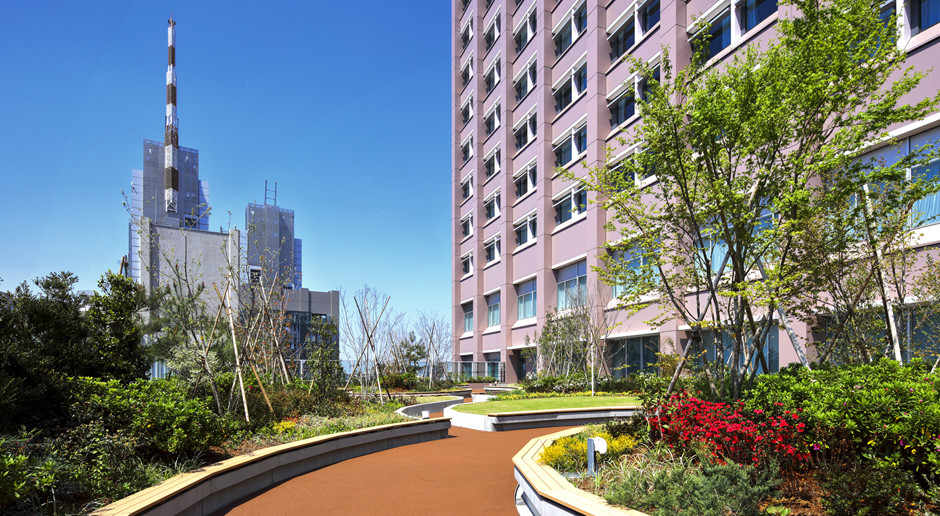

The rooftop garden provides a healing space for patients, their families, and staff.
Proof of world-class ecological construction
This state-of-the-art hospital takes the surrounding environment and global environment into consideration in many ways. It not only has architectonics such as small eaves on the south side and use of well water for the toilets and other equipment that uses non-potable water; all aspects of people and the environment have also been taken into consideration in terms of the daily practical operation and user comfort and convenience. Proof of that lies in the fact that this was the first hospital in Japan to obtain the LEED* (Healthcare) Gold certification, which is an international environmental standard.

*1 LEED: Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design
Developed and operated by the U.S. Green Building Certification Institute
A system for evaluating the environment performance of building and premises use

The information posted here is the current information on September 1, 2017.
Please be aware that this information may have changed by the time you view it.