Discussions have been moving forward in recent years on new international targets relating to biodiversity. Companies are also being asked to undertake ambitious efforts to contribute to the recovery of the natural environment.
The construction industry is an industry which affects the natural environment. On the other hand, it is also an industry which can contribute to its recovery.
The Shimizu Group quantifies the impact our business activities have on the natural environment and biodiversity. We are looking to eliminate any negative impact. Furthermore, we aim to realize a sustainability society where biodiversity is found in abundance by working on urban planning and social infrastructure development with green infrastructure.
Green Infrastructure + (PLUS)
We are working with our business concept being Green Infrastructure + (PLUS) to turn the expertise and technologies we possess into a “+.” This is based on the idea of green infrastructure which smartly utilizes the functions of nature and the potential of communities.
We value returning the blessings of nature to towns and communities in Green Infrastructure + (PLUS). We will continue in the future to strive to realize a sustainable society where people and living nature coexist. We will achieve that goal by working with external organizations while utilizing the technologies and expertise we have accumulated as Shimizu Corporation to conserve and create the natural environment and biodiversity with respect for ecosystems unique to communities.

Shimizu Biodiversity Guidelines
Shimizu led the industry in recognizing biodiversity as an important challenge in environmental management and formulated the Shimizu Biodiversity Guidelines in 2009 to continue and develop those activities further. We aim to preserve biodiversity and take the initiative on co-existing harmoniously with nature in all business areas to contribute to the realization of a sustainable society and pass the blessings and cultural value of biodiversity on to the next generation.
Shimizu Biodiversity Guidelines (PDF: 96 KB)
Basic Principle
Humankind is supported by the blessings of biodiversity which the planet has created over billions of years. Conserving that biodiversity is a challenge of this century which companies have to tackle along with measures against global warming.
Shimizu Corporation recognizes that biodiversity is the foundation of sustainable social activities. Accordingly, we are working on biodiversity as an important issue in environmental management. We will create an even greater environment through our construction activities by taking action with respect for nature and a global perspective.
We have established guidelines here. We aspire for coexistence between people and nature. We will pass on the blessings and cultural value from biodiversity to the next generation. These efforts will contribute to the realization of a sustainable society.
Guidelines
- 1. Stance of Initiatives
- We consider biodiversity to be an important issue in environmental management. We will voluntarily work to conserve and coexist with biodiversity in all our business areas. We will review those efforts as necessary and strive for improvement.
- 2. Initiatives in Construction Activities
-
- We will understand the environment of the community including the construction site and then carry out design and construction planning which take into consideration conservation and coexistence with biodiversity.
- We will understand our impact on the atmosphere, water and soil during construction. If there are concerns we will cause new impacts on biodiversity, we will strive to avoid and reduce them.
- We strive to procure goods in consideration of biodiversity based on the Green Procurement Guidelines.
- We will cooperate and collaborate with customers, governments, local communities, NPOs/NGOs, research institutions, companies and other organizations to undertake activities for the prevention of impacts on biodiversity caused by construction and for the conservation and sustainable use of biodiversity.
- 3. Compliance
- We will comply with laws and community needs concerning biodiversity based on high corporate ethics.
- 4. Education
- We will deepen understanding by providing education on the necessary knowledge, laws/ordinances and technologies concerning biodiversity to officers and employees of Shimizu Construction and group companies, and partner companies.
- 5. Information Disclosure
- We will disclose information concerning biodiversity in our corporate reports and on our website.
- 6. R&D
- We will conduct R&D concerning biodiversity. We will give back the results of that R&D to society.
- 7. Social Contribution
- We will participate in and collaborate with external activities concerning biodiversity. At the same time, we will provide opportunities for youth education.
List of Organizations We Are Participating in Relating to Biodiversity
We are proactively participating in committee and alliances relating to biodiversity with the aim of conserving and improving biodiversity.
Spread and Promotion of Biodiversity with Participation in Alliances
| Organization | Details of Activities | Logo |
|---|---|---|
| Japan Business Initiative for Biodiversity (JBIB) | We participate in various working groups. We are working on research and implementation relating to biodiversity conservation while engaging in dialogue with other companies and stakeholders. |  |
| Association for Business Innovation in harmony with Nature and Community | We are contributing to promoting the development of biodiversity-friendly green spaces by disseminating and raising awareness of a green space certification initiative called the Ikimono Kyosei Jigyosho ® (commonly known as the ABINC) |  |
| 30by30 Alliance | We are contributing to the achievement of the 30by30*1 international commitment with an all-Japan mindset. At the same time, we are cooperating with the implementation of other effective area-based conservation measure (OECM)*2 demonstration projects.
|
 |
In addition to the above, we endorse the Initiative on the Declaration of Biodiversity by Keidanren.
Initiatives that Consider Biodiversity in Business Activities
Research and Planning and Construction of Business Activities with Consideration for Biodiversity
At the planning and design stage, we require the mandatory drafting of an “architectural and civil engineering design eco map”. This mandatory eco map requires team members to identify and evaluate the biodiversity related key issues such as risks and opportunities and relevant laws and regulations. Moreover, where necessary team members are expected to conduct site-visits for the evaluation of ecosystems and conducting of relevant simulations, as well as consider policies and guidelines for the preservation of biodiversity and the creation of greener infrastructure that can be incorporated into the biodiversity preservation and enhancement plans. Draft biodiversity preservation and enhancement plans will be subject to a design review by the relevant executive design manager, and if approved, will be incorporated into the “design transfer sheet”, and passed on to the person in charge of construction.
Shimizu requires the mandatory drafting of a “key environmental area management chart” when beginning construction. This management chart explicitly incorporates items such as impact on ecosystem due to water pollution and issues identified regarding the ecosystem as environmental management indicators. If there are any material concerns regarding impact on biodiversity based on opinions obtained from relevant stakeholders – the client, the designer, the government and municipal offices, the local neighborhood, and academics, these concerns are deliberated on at the pre-construction committee meeting, where approval must be provided to proceed with the project.
Furthermore, during and after construction, project teams are expected to cooperate with relevant internal divisions to conduct monitoring over the local ecosystem. Project teams are also expected to recommend obtaining certifications such as ABINC, SEGES, and SITES to the client. If the client agrees to the recommendation, we will provide assistance to obtain the certification and enhance public visibility of the project’s greening efforts.
- Association for Bussiness Inovation In harmony with Nature and Community
- Social and Environment Green Evaluation System
- Sustainable SITES Initiative
UE-Net Evaluation of the Ecosystem Network in an Area
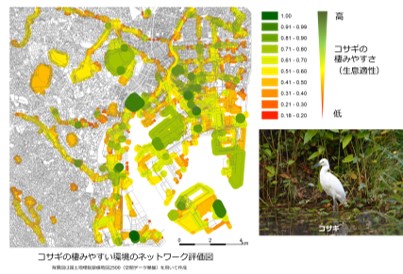
We develop and put to practical use the UE-Net (Urban Ecological Network). This is a simulation system which supports the formulation of development plans taking into consideration biodiversity in urban areas. We analyze the natural environment of the region using satellite image data to propose greening plans within business sites.
Japan Society of Civil Engineers FY 2012 Environmental Award, Engineering Advancement Association of Japan
Shimizu registers trademark on UE-Net.
Designing Biodiversity-conscious Spaces
Ecological Landscapes Draw on the Hidden Potential of Nature in Designing Spaces

Ecological landscape is a design method. We use it to accurately understand the natural resources possessed by a community and to then simultaneously consider the ecosystem, engineering and design of that place to find solutions. Through that, we conserve and create an environment which can only be formed in that community.
Construction with Consideration for the Biodiversity of Local Plants and Animals
Measures to Protect Plants and Animals During Construction of a Dam or Tunnel

Tunnel and dam construction is done in the abundant natural environment of mountainous areas, and is accompanied by major changes in the terrain and removal of trees. This has a major impact on the ecosystem, so we take various steps, depending on the particular characteristics of the natural environment, or the status of rare species living in the area. We also rely on the research and advice of a committee or other body consisting mainly of academic experts established to ensure protection of rare species as we proceed with construction.
- Environmentally-friendly Tunnel Construction (PDF: 748 KB) (only in Japanese)
- Dam Project Working to Protect the Ecosystem (PDF: 3.7 MB) (only in Japanese)
Examples of Biodiversity Preservation
Shimizu cleverly utilizes the functions of inherent in nature in building infrastructure and supports business activities that contribute to restoration of the blessings of nature and the creation of sustainable communities.
Preserving Biodiversity in Urban Areas
Yokohama Nomura Building



In the Yokohama Nomura Building in Minatomirai, Yokohama, which was completed in 2017, the client and the city of Yokohama set the goal of environmentally-friendly development that incorporated new greening technology.
We employed a team that consisted of all divisions of the Shimizu Group that are involved in ecosystems and the environment and met the needs of the client and the city of Yokohama by successfully employing the following five greening and environmental technologies in the project.
- The UE-Net biological habitat suitability simulation technology was used to evaluate the ecological network of the area before and after establishment to provide comparative verification and visualize it.
- The introduction of local plant varieties (genetic analysis technology) enables us to consider an ecosystem that is intrinsic to the area, without genetic disturbance.
- A depressed planting zone (rain garden) to collect rainwater was created, to promote the natural collection of rainwater and biodiversity in a marsh environment.
- A vertical louvered "green radiator" full of greenery was installed on the exterior walls with a wide variety of species intrinsic to Japan, including rare species.
- Green benches that would not obstruct the green area were installed, and an urban environment was created to provide a cool spot in summer and where people can experience the biodiversity.
These types of initiatives in preserving biodiversity in urban areas has enabled Shimizu to acquire certification under several environmental assessment systems such as the Organization for Landscape and Urban Green Infrastructure SEGES (Social and Environmental Green Evaluation System), LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design), and CASBEE (Comprehensive Assessment System for Built Environment Efficiency) certifications.




